|
PICSEL
1 project | PICSEL
2 project
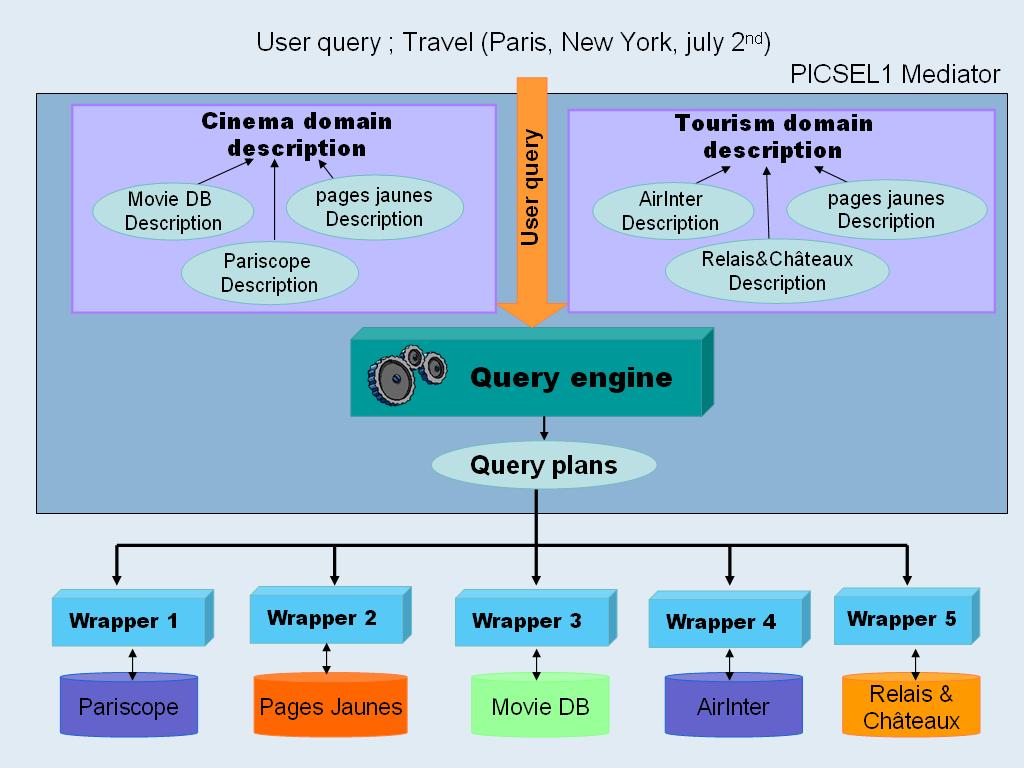
The approach
which has been chosen in PICSEL 1 is to define an information server
as a knowledge-based mediator in which CARIN is used as the core logical
formalism to represent both the domain of application and the contents
of information sources relevant to that domain. CARIN combines the expressive
power of rules and the ALN description logics. The expressive power
of the CARIN language is exploited in the PICSEL information integration
system, while maintaining the decidability of query answering.
PICSEL 1 contains a cooperative module to refine queries posed to a
mediator which gets no answer.
The general
architecture is shown below :
In PICSEL
2, we have focused on the automation of the construction of an ontology
in the context of a domain-specific mediator querying XML documents.
The ontology that we want to build is a schema based on classes. The
approach is based on the DTDs associated to the XML documents. Besides,
we have designed mediation systems which integrate services on the Web
in order to make them usable to final users. As services on the Web
are numerous and heterogeneous, as they must sometimes be combined to
satisfy final users requirements, interfaces giving the illusion of
a convivial, unique, centralized and homogeneous access are also necessary.
We have proposed to use a mediator approach to design such an interface
and we have emphasized the principles to make the mediator approach
applicable in this context. The first principle is a solution to semantic
heterogeneity. It exploits results in standardization relative to business
transactions. The second principle concerns the scalability of the mediator
approach. It emphasizes two points : decoupling of the various components
and strong mediation. We have proposed an architecture of a mediation
system integrating services, designed in the setting of the PICSEL 2
project. We have illustrated this approach with an application of e-commerce
in the tourism domain.
In PICSEL
2, we have also designed a user interface, the OntoRefiner system, for
helping the user to navigate numerous retrieved documents after a search
querying a semantic portal which integrates a very important number
of documents. Retrieved answers are filtered and the user could be provided
only with the answers which are, according to him, the most relevant.
The refinement process is based on two technologies, dynamic clustering
close to Galois lattice structure combined to the use of a domain ontology.
The Galois lattice structure provides a sound basis for the query refinement
process. However, its construction as a whole is a very costly process.
So, we have proposed an approach based on the use of a domain ontology,
avoiding the construction of the whole Galois lattice
|